Special Tests - Orthopedic Exam (A-Z)
- Head and Neck Special Tests:
- Shoulder Special Tests:
- Trunk and Abdomen Special Tests:
- Hip and Pelvis Special Tests:
- Knee Special Tests:
- Ankle and Foot Special Tests:
Choose and click on the Special Test among the list to see the Procedure, Positive Sign and Purpose of the assessment. In physical orthopedic examination, special tests are used to rule in or rule out musculoskeletal problems.
You may also keep scrolling down to view all the Special Tests.
HEAD & NECK Special Tests
- Anterior Neck Flexors Strength Test
- Anterolateral Neck Flexors Strength Test
- Cervical Compression Test
- Cervical Distraction
- First Rib Mobility Test
- Orbicularis Oculi Strength Test
- Posterolateral Neck Flexors Strength Test
- Sinus Transillumination Test
- Spurling’s Test
- Swallowing Test
- Three- Knuckle Test
- Upper Trapezius Strength Test
- Vertebral Artery Test
SHOULDER Special Tests
- Acromioclavicular Shear Test
- Adhesive Capsulitis Abduction Test
- Adson’s Test
- Costoclavicular Syndrome Test
- Drop Arm Test
- Eden’s Test
- Hawkin’s Kennedy Impingement
- Infraspinatus Strength Test
- Middle Trapezius Strength
- Neer Impingement
- Painful Arc Test
- Pectoralis Major Length
- Pectoralis Minor Length
- Rhomboids Strength
- Shoulder Adductors Length Test
- Speed’s Test
- Subscapularis Strength Test
- Supraspinatus Strength Test
- Travel’s Test
- Upper Limb Tension 1
- Upper Limb Tension 2
- Upper Limb Tension 3
- Upper Limb Tension 4
- Wright’s Hyperabduction Test
- Yergason’s Test
HIP & PELVIS Special Tests
- Ely’s Test
- Faber Test
- Gaenslen’s Test
- Gluteus Maximus Strength Test
- Hamstring Strength Test
- Hip Adductor Length
- Hip Quadrant Test
- Iliopsoas Strength Test
- Ober’s Test
- Pace Abduction Test
- Piriformis Length Test
- Posterior SI Joint Provocation
- SI Joint Gapping Test
- SI Joint Motion/ Gillet’s Test
- SI Joint Squish Test
- Straight Leg Raise Test
- Supine To Sit Test
- Thomas Test
- Trendelenburg’s Sign
KNEE Special Tests
- Apley’s Compression Test
- Apley’s Distraction Test
- Bragard’s Sign
- Clarke’s Patellofemoral Grind Test
- Coronary Ligamentous Stress Test
- Gravity Drawer Test (aka Posterior Sign)
- Helfet’s Test
- Lachman’s Test
- Major Effusion Test (aka Ballottable Patella)
- Minor Effusion Test ( aka Brush Test)
- McConnell’s Test
- McMurray’s Test
- Noble’s Test
- Patellar Apprehension Test
- Q ( Quadriceps ) Angle
- True Tibia and Femur Length Test
- Valgus Stress Test of the Knee
- Varus Stress Test of the Knee
- Waldron’s Test
Head and Neck Special Tests:
CERVICAL SPINE ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TESTS
Anterior Neck Flexors Strength Test
Purpose:
To asses the strength of the neck flexors (SCM, anterior scalene, supra and infrahyoids, longus colli and capitis, and rectus capitis anterior)
Procedure:
- Patient is supine
- Patient abducts arm to 90°, flexes the elbows to 90°, and rest their dorsal hands on the table.
- Patient tucks chin, and then lifts head off the table.
- Patient keeps the head lifted off the table (Grade 3). Patient resists therapist posteriorly-directed pressure (Grade 5)
Positive Sign:
Weakness of Anterior Neck Flexors if Patient is unable to keep the neck in flexion against gravity or the therapist’s pressure.
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
Anterolateral Neck Flexors Strength Test
Purpose:
To asses the strength of the Anterolateral Neck Flexors (SCM and scalene on one side).
Procedure:
- Patient is supine
- Patient abducts arm to 90°, flexes the elbows to 90°, and rest their dorsal hands on the table.
- Patient rotates the head away from the side being tested. Therapist stabilizes the side being tested.
- Patient lifts the head into slight flexion and hold it against gravity.
- Patient keeps the head lifted off the table (Grade 3).
- Therapist holds the temporal region on the side being tested.
- Therapist pushes in an oblique posterolateral direction, away from the tested side.
Positive Sign:
Weakness of the Anterolateral Neck Flexors if the patient is unable to keep the neck in flexion against gravity or the therapist’s pressure.
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
Cervical Compression Test
(for patients who cannot rotate or extend their head)
Testing For:
Compression of cervical nerve root or facet joint irritation in the Lower Cervical Spine
Procedure:
- Patient is seated.
- Patient’s head is in neutral.
- Therapist stands behind patient.
- Carefully apply compression downward on the head of the patient.
Positive Sign:
Radiating pain or other neurological signs in the same side arm (nerve root) and/ or pain local to the neck or shoulder (facet joint irritation).
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
Cervical Distraction
Purpose:
To relieve the pressure on the cervical nerve roots (may be used after Spurling’s or Cervical Compression Tests)
Procedure:
- Patient is supine or seated. Patient’s head is in a neutral position at all times throughout the procedure.
- Therapist grasps the patient’s head at occiput and temporalis. One hand on either side of the head.
- Slowly traction the patient’s head in a superior direction. Maintain the traction for at least 30 seconds.
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
First Rib Mobility Test
Purpose:
To test the mobility of Rib 1
Procedure:
- Patient is seated.
- Patient fully rotates their head away from the side being tested.
- Patient then fully flexes the head to their chest.
Positive Sign:
Patient has limited neck flexion. The cause for the hypomobilty may be tight scalenes.
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
Orbicularis Oculi Strength Test
Purpose:
To confirm Bell’s Palsy
Procedure:
- Patient seated. Patient keeps their eyes closed.
- Therapist tries to slowly open the patient’s eye on the affected side with their clean hands.
Positive sign:
Patient cannot keep their eyes closed against therapist’s resistance.
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
Posterolateral Neck Flexors Strength Test
Purpose:
To asses the strength of the Posterolateral Neck Flexors (splenius capitis and cervicis, semispinalis capitis and cervicis, cervical Erector Spinae on one side)
Procedure:
- Patient is supine
- Patient abducts arm to 90°, flexes the elbows to 90°, and rest their dorsal hands on the table.
- Patient extends their neck. Therapist stabilizes the side being tested.
- Patient then rotates the head towards the side being tested.
- Patient holds the head in this position.
- Patient keeps the position against gravity (Grade 3).
- Therapist holds temporalis area of the unaffected side, then pushes in an oblique posterolateral direction, away from the tested side.
Positive Sign:
weakness of the Posterolateral Neck Flexors if the patient is unable to hold their neck against gravity or the therapist’s pressure.
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
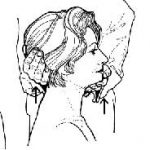
Sinus Transillumination Test
Testing For:
Infection of the frontal and maxillary sinuses
Procedure:
- Test is performed in a dark room
- Use a bright flashlight. Cover the flashlight with transparent and clean plastic bag
- Maxillary Sinus: Patient places the flashlight inside the mouth, against the roof of the mouth.
- Frontal Sinus: Using a different clean plastic bag, place flashlight against the medial aspect of the eyebrows.
Positive sign:
Sinuses are infected or blocked if they do not glow red (transilluminate). A normal sijus shows a red glow in the area occupied by the sinus.
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
Spurling’s Test
Testing For:
Compression of a cervical nerve root or facet joint irritation in the Lower Cervical Spine
Procedure:
- Patient is seated. Therapist stands behind patient.
- Patient slowly extends, sidebends, and rotates the head to the affected side.
- Therapist carefully apply compression downward on the head of patient.
Positive Sign:
Radiating pain or other neurological signs in the same side arm (nerve root) and/ or pain local to the neck or shoulder (facet joint irritation).
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
Swallowing Test
Purpose:
To see if the cause of the pain when swallowing, is trigger points on the SCM
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Palpate and Pincer grasp SCM. Locate the most tender point.
- Place a firm pressure on the most tender point (muscle belly) and have the patient swallow
Positive Sign:
pain diminishes when the patient swallows as you pincer grasp the most tender point
Otherwise:
pain may be caused by throat infection, hematoma, bony protruberance of the cervical spine or tumor so patient should be advised to see a medical doctor.
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
Three- Knuckle Test
Testing For:
The available active range of depression of the mandible or TMJ hypomobility
Procedure:
- Tell Patient to open jaw
- Ask them to insert as many of their own flexed proximal interphalangeal joints of the non-dominant hand
Positive Sign:
Patient can only get one knuckle or knuckles between their teeth.
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
Upper Trapezius Strength Test
Purpose:
To asses the strength of the Upper Trapezius Muscle
Procedure:
- Patient is supine
- Patient abducts arm to 90°, flexes the elbows to 90°, and rest their dorsal hands on the table.
- Patientextends their neck. Therapist stabilizes the side being tested.
- Patient then rotates the head away the side being tested.
- Patient holds the head in this position.
- Patient keeps the position against gravity (Grade 3).
- Therapist apply pressure on the posterior head, slightly pushing the head anteriorly and obliquely away from the tested side.
- Patient tries to resist therapist’s pressure (Grade 5)
Positive Sign:
Weakness of the Upper Trapezius if the patient is unable to hold their neck against gravity or the therapist’s pressure.
ORTHOPEDIC TEST/ SPECIAL TEST:
Vertebral Artery
Testing For:
Ischemia or Circulation deficiency of the vertebral artery at the transverse foramen
Procedure:
- Patient seated
- Patient actively rotates the head fully to one side, then extends the neck
- Hold for 30 seconds
- Do the same on the other side
Positive sign:
Patient complains of dizziness, nystagmus, or both. (Further testing is contraindicated and patient must be referred to a medical doctor).
Shoulder Special Tests:
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Acromioclavicular Shear Test
Testing for:
the integrity of the acromioclavicular joint
Procedure:
- Patient is seated.
- Therapist stands behind the patient.
- Place cupped hands over the patient’s shoulder, the fingers interlaced. One palm on the clavicle, the other hand on the scapula.
- Slowly squeeze the heels of the hands together.
Positive Sign:
Pain or excessive movement of the acromioclavicular joint
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Vocal Fremitus Test
(fremitus = palpable vibration on the human body)
Purpose: to assess for areas of bronchial congestion (usually with mucus, serum or lymph) due to Chronic Bronchitis or Emphysema
Procedure:
- Patient is prone
- Instruct patient to repeat the words “ blue balloons” or “ ninety nine” (low frequency vocalizations).
- At the same time, therapist places both hands symmetrically over the patient’s thorax, moving them over the lungs and bronchi assessing for the presence of vocal fremitus or palpable vibrations in the lungs.
Positive Sign: decreased vibration in areas of the lungs that has congestion.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Adhesive Capsulitis Abduction Test
Testing for:
Frozen Shoulder. Restricted motion at the shoulder caused by fibrosing and adhesion of the axillary fold of the inferior Glenohumeral Joint Capsule.
Procedure:
- Patient is seated.
- Therapist stands behind the patient
- Therapist palpates inferior angle of scapula and monitor its movement throughout the test
- With the therapist’s other hand, holding just above patient’s elbow, slowly abduct the patient’s humerus
- Therapist takes note of when the inferior angle of the scapula starts to move
Positive Sign:
Painful, leathery end feel before 90° of abduction
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Adson’s Test
Testing for:
Neurovascular Compression (TOS) caused by the anterior scalene.
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Passively extend and slightly externally rotate their affected arm
- Monitor their radial pulse
- Patient rotates their head towards the affected side, slightly elevate their chin
- Patient takes a deep breath and holds it from 15-30 seconds.
Positive Sign:
Patient’s symptoms reoccur (numbness, tingling in hands and fingers) or the patient’s radial pulse diminishes.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Costoclavicular Syndrome Test
Testing for:
Neurovascular Compression (TOS) between the clavicle and Rib 1.
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Monitor their radial pulse on the affected arm
- Passively depress and retract the shoulder of the affected arm
Positive Sign:
Patient’s symptoms reoccur (numbness, tingling in hands and fingers)or The patient’s radial pulse diminishes.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Drop Arm Test
Testing for:
the integrity of the rotator cuff, especially the supraspinatus muscle and tendon
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Patient actively abducts their humerus to 90° and keeps their arm in this position
- Patient slowly and smoothly adducts their arm back
Positive Sign:
Pain or the Patient cannot slowly and smoothly adduct their arm back to the side
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Eden’s Test
Testing for:
Neurovascular Compression (TOS) between the clavicle and Rib 1.
Procedure:
- Patient is standing
- Monitor their radial pulse on the affected arm
- Patient depresses and retracts the shoulder of their affected arm
Positive Sign:
Patient’s symptoms reoccur (numbness, tingling in hands and fingers) or The patient’s radial pulse diminishes.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
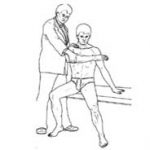
Hawkin’s Kennedy Impingement Test
Testing for:
Overuse injury to the supraspinatus tendon
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Patientflexes their arm to 90° then internally rotates their humerus
Positive Sign:
Pain in the acromion / tendon area
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Infraspinatus Strength Test
Testing for:
Tendonitis, Strain or Weakness of the Infraspinatus/ Teres Minor muscles
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Patient actively abducts their humerus to 90°
- Patient flexes their elbow to 90°
- Therapist applies pressure into internal rotation, patient resists and tries to externally rotate their humerus
Positive Sign:
Pain along infraspinatus or weakness
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Middle Trapezius StrengthTest
Testing for:
the strength of the middle trapezius muscle
Procedure:
- Patient is prone
- Patient affected shoulder to 90°
- Patient externally rotates arm
- Patient attempts to extend their affected arm then hold (grade 3 strength)
- therapist stabilizes unaffected shoulder
- Patient attempts to extend their affected arm as the therapist resists (grade 5 strength)
Positive Sign:
The patient’s cannot hold the arm in extension or cannot resist the therapist anteriorly directed pressure
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Neer Impingement Test
Testing for:
Overuse injury to the supraspinatus tendon
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Passively flex their affected humerus through its range
Positive Sign:
Pain in the acromion / tendon area
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Painful Arc Test
Testing for:
Impingement of the supraspinatus tendon and subacromial bursa beneath the acromion
Procedure:
- Patient actively and slowly abducts their humerus through its entire range
Positive Sign:
Pain in the acromion area starting at 70° of abduction, and eases after 130°
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Pectoralis Major Length Test
Testing for:
the length of the pectoralis major muscle
Procedure:
- Patient is supine …
A. Testing Clavicular Fibers:
- Patient abducts shoulder to 90°
Positive Sign for Clavicular Fibers: Arm does not drop below the table level
B. Testing Sternal Fibers:
- Patient abducts shoulder to 150°
Positive sign for Sternal Fibers: arm does not drop below the table level
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Pectoralis Minor Length Test
Testing for:
the length of the pectoralis minor muscle
Procedure:
- Patient is supine, with their arms on their sides
- Therapist stands or sits at the head of the table
- Observe the patient’s shoulder protraction
- (Therapist may try to retract the affected shoulder)
Positive Sign:
The patient’s affected shoulder is protracted or limited Range of shoulder retraction
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Rhomboids Strength Test
Testing for:
the strength of the rhomboid muscles
Procedure:
- Patient is prone
- Patient affected shoulder to 90°
- Patient internally rotates arm
- Patient attempts to extend their affected arm then hold (grade 3 strength)
- therapist stabilizes unaffected shoulder
- Patient attempts to extend their affected arm as the therapist resists (grade 5 strength)
Positive Sign:
The patient cannot hold the arm in extension or cannot resist the therapist anteriorly directed pressure
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Shoulder Adductors Length Test
Testing for:
the length teres major and latissimus dorsi muscles
Procedure:
- Patient is supine
- Patient flexes their hips and knees, and have their feet rest on the table
- Patient fully flexes their arms above the head
Positive Sign:
The patient’s arms are not able to reach and rest on the table
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Speed’s Test
Testing for:
the presence of Biceps Tendonitis
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Patient completely extends their elbow then supinates their arm
- Therapist stabilizes at the shoulder
- Patient attempts to flex the elbow while Therapist holds patient’s forearm and applies resistance
Positive Sign:
Pain at the biceps tendon area during resistance
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Subscapularis Strength Test
Testing for:
Tendonitis, Strain or Weakness of the Subscupularis muscle
Procedure:
- Patient is seated, their affected arm at their side
- Patient flexes their elbow to 90°
- Therapist applies pressure in external rotation, patient resists and tries to internally rotate their arm
Positive Sign:
Pain along the subscapularis or weakness
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Supraspinatus Strength Test (Empty Can Test)
Testing for:
Tendonitis, Strain or Weakness of the Supraspinatus muscle
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Patient actively abducts their humerus to 90°
- Patient adducts their humerus to 30°
- Patient internally rotates their humerus
- Therapist applies pressure in adduction, patient resists
Positive Sign:
Pain along the supraspinatus or weakness
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Travel’s Test
Testing for:
Neurovascular Compression (TOS) caused by the middle scalene.
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Passively extend and slightly externally rotate their affected arm
- Monitor their radial pulse
- Patient rotates their head away from the affected side
- Patient takes a deep breath and holds it from 15-30 seconds.
Positive Sign:
Patient’s symptoms reoccur (numbness, tingling in hands and fingers)or The patient’s radial pulse diminishes.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
ULTT1 (Upper Limb Tension Test 1)
Testing For:
C5, C6, C7 nerve roots and median nerve as the source of the patient’s painful shoulder and arm
Procedure:
- Patient is supine , with their side being tested at the edge of the table
- Apply a depressive force to the patient’s affected shoulder
- With your other hand, hold the patient’s wrist and Abduct their affected humerus to 110°
- Extend their arm to 10° below the coronal plane and, to 60° of external rotation
- Slowly extend their wrist and fingers
- Fully supinate their forearm then slowly extend their elbow
- ( you may flex their neck laterally to the opposite side if the above does not show up positive)
Positive Sign:
Recurrence of their shoulder and arm pain.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
ULTT2 (Upper Limb Tension Test 2)
Testing For:
the Median nerve, Musculocutaneous Nerve, and Axillary Nerve as the source of the patient’s painful shoulder and arm
Procedure:
- Patient is supine, with their side being tested at the edge of the table
- Apply a depressive force to the patient’s affected shoulder
- With your other hand, hold the patient’s wrist and Abduct their affected humerus to 10°
- Slowly extend their wrist and fingers
- Fully supinate their forearm then slowly extend their elbow
Positive Sign:
Recurrence of their shoulder and arm pain.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
ULTT3 (Upper Limb Tension Test 3)
Testing For:
the Radial nerve as the source of the patient’s painful shoulder and arm
Procedure:
- Patient is supine , with their side being tested at the edge of the table
- Apply a depressive force to the patient’s affected shoulder
- With your other hand, hold the patient’s wrist and Abduct their affected humerus to 10°
- Slowly flex their wrist and fingers, then deviate the wrist to the ulnar side
- Fully pronate their forearm then slowly extend their elbow
Positive Sign:
Recurrence of their shoulder and arm pain.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
ULTT4 (Upper Limb Tension Test 4)
Testing For:
C8 and T1 nerve roots and ulnar nerve as the source of the patient’s painful shoulder and arm
Procedure:
- Patient is supine , with their side being tested at the edge of the table
- Apply a depressive force to the patient’s affected shoulder
- With your other hand, hold the patient’s wrist and Abduct their affected humerus to 90°
- Slowly flex their elbow, then supinate their forearm
- Slowly extend their wrist and fingers and deviate the wrist to the radial side.
Positive Sign:
Recurrence of their shoulder and arm pain.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Wright’s Hyperabduction Test
Testing for:
Neurovascular Compression (TOS) caused by the pectoralis minor.
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Passively abduct their affected arm to 180°, then slightly extend the arm.
- Monitor their radial pulse on the abducted arm
Positive Sign:
Patient’s symptoms reoccur (numbness, tingling in hands and fingers)or The patient’s radial pulse diminishes.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Yergason’s Test
Testing for:
the stability of the biceps tendon and integrity of the transverse humeral ligament
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Therapist’s one hand stabilizes the patient’s elbow against the patient’s body
- Therapist’s other hand applies resistance as the patient actively supinates their forearm, extends their elbow, and externally rotates the humerus
Positive Sign:
Pain at the area of the bicipital groove
Trunk and Abdomen Special Tests:
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
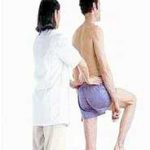
Functional or Structural Scoliosis Test
Purpose: To find out whether the spinal curvature is functional or structural.
Procedure:
- Patient is standing
- Observe the location and movement of the patient’s spine and curvature
- Ask patient to laterally bend their trunk on both sides slowly, then flex their trunk slowly
Positive Signs:
Functional Scoliosis: if the curvature fixes itself (reverses) as the patient laterally bends towards the convex side
Functional Scoliosis: if the curvature and rib humping reverse as the patient bends forward
Structural Scoliosis: the curvature does not correct itself as the patient laterally bends towards the convex side, and the curvature remains
Structural Scoliosis: if the curvature and rib humping remains the same as the patient bends forward
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Kemp’s Test
Testing for: Nerve root compression, due to disc herniation or facet joint irritation in the lumbar spine
Procedure:
- Patient is standing
- Patient actively and slowly extends, sidebends and rotates their thorax and lumbar spine to the affected side.
- Therapist may apply an inferiorly directed pressure to the shoulder on the affected side (Quadrant’s Test)
Positive Sign:
Nerve root compression: Radiating pain or other neurological signs in the affected leg.
Lumbar Facet Joint irritation: Pain local to the back
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Kernig’s Test
Purpose: to stretch the spinal cord and the dural tube to reproduce the pain caused by nerve root involvement or meningeal irritation.
Procedure:
- Patient is supine, with their hands behind their head.
- Patient actively flexes their head into their chest.
- Then, with their knees in extension, patient flexes their hip.
Positive Sign:
Meningeal irritation: Pain along the spine in the level of lesion
Nerve root involvement: Pain in a referral pattern to a limb
Patient may flex their knee or remove their head from flexion to reduce the stretch on the dural tube to reduce the pain
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Quadratus Lumborum Length Test
Testing for: the length of the Quadratus Lumborum muscles
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Therapist stands behind the patient and landmarks both iliac crests
- Patient slowly bends their torso laterally away from the tested side, then toward the tested side
- Therapists notes the Range of Motion on both lateral bending
Positive Sign: reduced range of motion or restriction when bending away from the tested side.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Rebound Tenderness
Testing for: possible presence of appendicitis or peritoneal inflammation
Procedure:
- Patient is supine, their hips and knees are flexed
- Slowly apply pressure over Mc Burney’s point and the quickly release the pressure
- Mc Burney’s point: two-thirds distance inferiorly along an imaginary line drawn from the umbilicus and the right ASIS.
Positive Sign:
Severe pain when pressure is released. (Symptoms may be accompanied by nausea and low grade fever).
This is a medical emergency. Massage is contraindicated with a Positive test result.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Scoliosis Short Leg
Purpose: to see if patient has an uneven leg length that is causing functional scoliosis
Procedure:
- Patient is standing
- Observe the patient’s Bilateral Iliac Crests and Acromioclavicular joints levels, and see if there is tilting and scoliosis.
- Place a thin book under the shorter leg
Positive Sign: the scoliosis curve reverses and neutralizes after the book was placed under the side with the shorter leg.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Scoliosis Small Hemipelvis
Testing for: Functional scoliosis due to the presence of a small hemipelvis . Hemipelvis* – one side of the pelvis.
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Observe the patient’s Bilateral Iliac Crests and Acromioclavicular joints levels, and see if there is tilting and scoliosis.
- Place a thin book under the lower (smaller) pelvis side.
Positive Sign: the scoliosis curve reverses and neutralizes after the book was placed under the side with the lower pelvis.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Slump Test
Purpose: to stretch the spinal cord and the dural tube to reproduce the pain caused by nerve root involvement or meningeal irritation
Procedure:
- Patient is seated and slumped into flexion
- Patient actively flexes their head to their chest
- Patient actively extends right knee then dorsiflexes the right foot. Do the left side afterwards.
Positive Sign:
Meningeal irritation: Pain along the spine in the level of lesion
Nerve root involvement: Pain in a referral pattern to a limb
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TEST:
Valsalva’s Test
Testing for: the presence of a space-occupying lesion (may be tumor, herniated disc, osteophytes) that is increasing the pressure within the spinal canal.
Procedure:
- Patient is seated and curled forward.
- Patient takes a breath while bearing down, as if moving the bowels
Positive Sign: pain local to the lesion site or radiating pain in a dermatomal pattern.
Hip and Pelvis Special Tests:
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Ely`s Test
Testing for: Rectus Femoris Contracture or Shortness
Procedure:
- Patient is prone
- Flex patient’s affected knee
- Try to bring the heel to the glutes
- Make sure their affected leg does not abduct
Positive Sign: the pelvis on the affected side flexes as you try to get the heel touch their glute (affected side)
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Faber Test
Testing for: hip pathology and psoas muscle shortness/spasm
Procedure:
- Patient is supine and their legs are extended
- Place Patient’s foot of the affected side on the other knee
Positive Sign: The affected hip stays above level of the unaffected knee
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Gaenslen’s Test
Testing for: Hip or Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
Procedure:
- Patient is sidelying on the unaffected side
- Patient flexes the hip and knee of the unaffected leg towards their chest
- Therapist is behind the patient, stabilizes patient’s pelvis with onehand
- Therapist hyperextends the patient’s affected leg at the hip
Positive Sign: Pain in the hip and Si joint area
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Gluteus Maximus Strength Test
Testing for: strength of the gluteus maximus
Procedure:
- Patient is prone
- The Patient’s knee on the affected side is flexed 90°
- Therapist stabilizes the affected hip with one hand
- Patient extends the affected hip and holds the hip/leg in extension
- If patient can hold their hip in extension against gravity, it indicates Grade 3 on the strength scale
- Therapist tries to put a downward pressure as the patient tries to hold their affecte hip in extension
- Patient can resist the therapist pressure indicates Grade 5 strength
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Hamstring Strength Test
Purpose: to locate hamstring strain
Procedure:
- Patient is prone, and their knees are flexed around 70°
- Therapist stabilizes the affected pelvis and the posterior tibia on the affected side
- Assess Medial Hamstrings (semitendinosus and semimembranosus) – slightly internally rotate femur. Patient holds this position against gravity (Grade 3 strength). As patient holds the position, therapist attempts to extend the affected knee.
Positive Sign – pain deep in the hamstrings indicates strain in the semimembranosus muscle while pain that is more superficial indicates strain in the semitendinosus muscle
- Assess Lateral Hamstring (biceps femoris) – slightly externally rotate patient’s femur and holds their knee in 70° flexion against gravity (Grade 3 strength). As patient holds the position, therapist attempts to extend the affected knee.
Positive Sign – pain in the lateral hamstrings indicates biceps femoris strain
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Hip Adductor Length Test
Assessing For: the length of the adductor muscles
Procedure:
- Patient Is supine
- Patient places the plantar surface of their foot on the medial aspect of the knee on the unaffected side. The affected hip is abducted, flexed and internally rotated and their affected knee is flexed.
- Stabilize the hip on the unaffected side as you apply a posterolaterally directed pressure on the affected knee
Positive Sign: hip adductors shortness indicated with reduced range of motion of the affected femur when you apply the posterolaterally directed pressure
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Hip Quadrant Test
Testing for: joint capsule tightness or hip pathology
Procedure:
- Patient is supine
- Therapist Flexes and adducts the patient’s affected hip, until there is some resistance
- Therapist maintain the resistance and moves the patient’s hip through an arc into abduction
Positive Sign: pain, early leathery end feel, crepitus in the movement
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Iliopsoas Strength Test
Testing for: iliopsoas weakness
Procedure:
- Patient is supine, with their knees in extension
- Stabilize the unaffected pelvis
- Patient flexes their affected hip at 30° and slightly externally rotates it
- Patient holds this position (Grade 3 strength)
Positive Sign: Patient cannot hold the affected leg off the table (in flexion and slight external rotation). To test Grade 5 Strength, therapist may try to put a downward pressure as the patient tries to keep the leg off the table in resistance.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Ober’s Test
Assessing For: the length of the Iliotibial band and Tensor Fascia Lata
Procedure:
- Patient is sidelying close to the edge of the table on the unaffected leg. Therapist stands behind the Patient.
- Flex hip and knee of the unaffected leg that is at the bottom
- Stabilize the Patient’s pelvis with one hand
- With the other hand grasping the medial aspect of the patient’s affected knee, passively hyperabduct and extend the affected femur at the hip.
- Allow the affected leg to lower without rotating
Positive Sign: the affected leg stays abducted and does not lower.
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Pace Abduction Test
Testing for: the strength of the piriformis muscle
Procedure:
- Patient is seated, with their hips flexed 90 ° and their knees together
- Therapist places both hands on the lateral side of the knees , holding them together
- Patient attempts to move their knees apart while the therapist resists
Positive Sign: piriformis weakness if the patient cannot move their knees apart. Pain is present in the area of the piriformis indicates piriformis trigger points
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Piriformis Length Test
Assessing For: the length of the piriformis muscle
Procedure:
- Patient is prone with their knees close together
- Patient flexes both their knees to 90°
- Slowly separate the lower legs away from the midline, while keeping the knees together (the internal rotation of the femur stretches both piriformis muscles)
- The normal internal rotation would be (45°-50°) from the midline
Positive Sign: short piriformis muscle is indicated if the internal rotation is less than 45°
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Posterior SI Joint Provocation
Testing for: SI joint dysfunction
Procedure:
- Patient is sidelying on the unaffected side
- Therapist brings affected hip into flexion
- Therapist places one hand on the patient’s ASIS on the affected side, and therapist other hand on the ischial tuberosity on the same side
- Therapist attempts to posteriorly rotate the patient’s affected pelvis
Positive Sign: pain around the SI joint indicates SI joint dysfunction
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
SI joint Gapping Test
Purpose: to assess the integrity of the anterior ligaments of the SI joints
Procedure:
- Patient is supine
- Therapist applies a lateral and inferior pressure to the medial sides of the patient’s Anterior Superior Iliac Spines. (Therapist crosses their arm in order to push easier)
Positive Sign: anterior ligament sprain if there is Unilateral Gluteal or Posterior Leg Pain
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
SI joint motion or Gillet’s Test
Testing for: Mobility of the Sacroiliac joint
Procedure:
- Patient is standing, may hold on to something for stability
- Therapist is behind the patient. Therapist palpates the PSIS of the patient’s affected side with their thumb
- Therapist places their other thumb on the S2 process of the patient’s sacrum
- Patient flexes the hip and knee of the affected side, raising their knee as high as they can, while standing on the unaffected side.
Positive Sign: SI joint hypomobility if the thumb on the affected side moves superiorly instead of inferiorly as the knee lifts
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
SI joint Squish Test
Purpose: to assess the integrity of the posterior ligaments of the SI joints
Procedure:
- Patient is supine
- Therapist places one hand on the lateral side of each of the patient’s Anterior Superior Iliac Spines
- Therapist apply pressure from lateral to medial (45 °) and then posteriorly.
Positive Sign: pain local to the Sacroiliac joint indicates posterior SI ligament sprain
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Straight Leg Raise
Purpose: To determine the cause of low back pain
Procedure:
- Patient is supine.
- Place their affected leg in adduction and internal rotation
- Raise the affected leg by grasping it around the heel and flexing the hip (their affected knee should be extended).
- Flex the hip until the patient feels pain (usually around 70-80 degrees of flexion)
- Slowly lower the leg until no pain is felt by the patient.
- Dorsiflex the patient’s affected foot (this stretches their sciatic nerve)
Positive Signs:
Hamstring Tightness – pain in the back of their thigh and knee during hip flexion
Lumbar or SI Joint Dysfunction – pain in the low back after 70 degrees of hip flexion only (no foot dorsiflexion)
Sciatic Nerve Involvement – pain down the leg during passive dorsiflexion
Space Occupying Lesion or Disc Herniation – pain down their opposite leg ( the one that is not raised)
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Supine to Sit Test
Testing for: Functional leg length discrepancy
Procedure:
- Patient is supine and knees are extended
- Therapist compares the levels of both malleoli
- Patient sits up while therapist takes a note of the malleoli levels
Positive Sign:
- Anterior Hip bone Rotation: One leg is longer when patient is supine, then shorter when patient is stting up
- Posterior Hip bone rotation: One leg is shorter when patient is supine, then longer when patient is sitting up
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Thomas Test
Testing for: Hip flexor muscle contracture or shortness
Procedure:
- Patient is supine , with lower gluteal folds at the end of the table and their hips and knees flexed. Patient may hold the legs in flexion with their hands.
- Therapist makes sure that the patient’s lower back is not so high off the table.
- Patient keeps the unaffected leg flexed, and slowly lowers the affected leg and lets it extend as far as it can
Positive Sign:
- Short QUADS: the affected knee stays extended
- Short Psoas muscles: the hips remains flexed
- Short TFL/ ITB: Abducted hip
ORTHOPEDIC EXAM/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Trendelenburg’s Sign
Testing for: the strength of the Gluteus Medius Muscle
Procedure:
- Patient is standing
- Therapist stands behind patient, paying attention to the patient’s PSIS and iliac spines
- Patient stands on the affected leg
Positive Sign: gluteus medius is weak if the pelvis on the affected side pops out or drops
Knee Special Tests:
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
True Tibia and Femur Length Test:
Testing for:
The tibia and femur lengths
Procedure:
- Patient is prone
- Patient’s knees and hips flexed , with the plantar surfaces of their feet on the table
- Their medial malleoli even and knees together
To compare the lengths:
Tibia: Therapist stands at the foot of the table to compare the heights of the patient’s tibial plateaus to look for the shorter tibia
Femur: Then therapist stands at the side of the table to compare the positions of the patellas looking for the shorter femur.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Noble’s Test
Testing for:
The presence of iliotibial band (ITB) friction syndrome
Procedure:
- Patient is supine, with both their affected side’s knee and hip flexed to 90° degrees
- Therapist compresses the iliotibial band (ITB) — 2 centimetres proximal to the lateral femoral condyle
- Instruct the patient to extend the knee and hip slowly while therapist maintains compression of the ITB proximal to the lateral femoral condyle
Positive Sign:
Pain over the lateral femoral condyle at about 30° degrees of knee extension.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Gravity Drawer Test (aka Posterior Sign)
Purpose:
To assess the integrity of the posterior cruciate ligament
Procedure:
- Patient is supine,
- their hips flexed to 45 degrees and
- their knees flexed to 90 degrees and
- their feet are flat on the table
- Observe the profile of both knees from the side of the table
Positive Sign:
The affected tibia sags posteriorly compared to the unaffected knee. (In given position, the tibia drops posteriorly on the femur if the posterior cruciate ligament’s integrity is compromised)
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Waldron’s Test
Testing for:
The Presence of patellofemoral syndrome
Procedure:
- Patient is standing
- Therapist palpates the patella while the patient performs knee bends
Positive Sign:
Presence of pain, crepitus, poor patellar tracking
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Major Effusion Test (aka Ballottable Patella)
Purpose:
Usually performed after an injury to assess for a major increase in the synovial fluid or blood within the knee joint capsule
Procedure:
- Patient is supine, the affected knee is extended as much as possible (with effusion, patient may not be able to extend their knee fully)
- Therapist gently extends the knee further, then compresses the patella down on to the condyles then release
Positive Sign:
Patella clicks onto the femur and then rebounds to the floating position. This could be caused by torn cruciate ligaments, meniscal tearing, or fracture and is considered a Medical Emergency. (Joint effusion within two hours of injury might be caused by blood in the joint, and joint effusion with synovial fluid usually develops 8 hours after injury.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Minor Effusion Test (aka Brush Test)
Purpose:
To assess for lesser amounts of synovial fluid within the knee joint right after an injury. This is usually done after the Major Effusion Test comes up negative.
Procedure:
- Patient is supine, their affected knee is extended as much as they can
- Therapist slowly sweeps the effusion from the superior lateral aspect of the knee and suprapatellar pouch
Positive Sign:
A bulge inferior to the patella appears within two seconds, the positive test will indicate from 4-8 millimeters of extra synovial fluid within the joint. This could be caused by cruciate or meniscal damage and is considered a Medical Emergency.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Q (Quadriceps ) Angle
Note: The Q angle is the angle between the quadriceps tendon and the patellar tendon. The Q-angle is formed from a line drawn from the ASIS to the center of the kneecap, and from the center of the kneecap to the tibial tubercle. To find the Q-angle, measure that angle, and subtract from 180 degrees.
To Measure Q Angle:
- Patient is standing, with the knee in extension and
- femur neutral: (no internal or external rotation) and
- patient’s feet in a neutral position (no pronation or supination)
Normal Q Angle Test Result:
A normal Q angle with the knee extended and the quadriceps muscle relaxed is 18° degrees for women and 13° degrees for men.
A Q angle that is less than normal allows the patella to track medially between femoral condyles, placing extra stress on the medial articulating facets of the patella which leads to Chondromalacia Patellae
A Q angle that is greater than normal allows the patella to track laterally, stressing the lateral facets which is associated with patellar tracking dysfunction, chondromalacia patellae and patellar subluxation.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Valgus Stress Test of the Knee
Testing for:
The integrity of the structures that prevent Valgus deformity of the knee (Joint capsule, medial collateral ligament, cruciate ligaments)
Procedure:
- Patient is supine
- Place the affected leg in extension and slight external rotation.
- Stabilize with one hand on the medial malleolus and with the other hand stabilize the lateral aspect of the knee
- Apply a medially directed stress on the lateral knee
- Flex their knee to 30 degrees and apply the same pressure on the lateral side to isolate the medial collateral ligament
Positive Sign:
Presence of pain and hypermobility at the medial aspect of the knee
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Varus Stress Test of the Knee
Testing For:
The integrity of the structures that prevent lateral instability at the knee (lateral collateral ligament, joint capsule, cruciate ligaments).
Procedure:
- Patient is supine with the affected knee in full extension.
- Therapist stabilizes the affected leg in slight external rotation with one hand on the lateral malleolus.
- Therapist places their other hand on the medial aspect of the knee.
- Therapist applies a laterally directed (a varus) stress on the medial knee.
- Flex their knee to 30 degrees and apply the same pressure on the lateral side to isolate the lateral collateral ligament
Positive Sign:
Presence of pain and hypermobility at the lateral aspect of the knee
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Lachman’s Test
Testing for :
The integrity of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL). The Lachman’s test is considered to be the most accurate test for ACL integrity.
Procedure 1:
- Patient is supine
- Patient’s affected knee is flexed 30°
- Therapist stabilizes distal femur with one hand while grasping patient’s proximal tibia with the other hand
- Therapist applies an anteriorly directed stress the tibia.
Procedure 2:
- Patient is seated with their affected leg over the edge of the table
- Therapist sits in front of the patient, supporting the patient’s ankle on therapist’s thigh
- Therapist places patient’s knee in 30° flexion
- Therapist stabilizes the distal femur with one hand
- Therapist applies anteriorly directed stress on the proximal tibia with the other hand
Positive Sign:
Pain or excessive anterior motion of the tibia, and disappearance of the infrapatellar tendon slope.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Patellar Apprehension Test
Purpose:
To test whether the patella is likely to dislocate laterally
Procedure:
- Patient is supine with their affected knee extended
- Therapists uses a slow and moderate pressure against the medial aspect of the patella moving it in a lateral direction
- Therapist observes patient’s reaction
Positive Sign:
Patient expresses apprehension and/ or might try to move their affected knee away from the pressure.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Helfet’s Test
Testing for:
The dynamic rotary function of the Tibia (possible torn meniscus or injured cruciate ligament)
Procedure:
- Patient is seated, with their legs hanging over the edge of the table
- Patient’s knees flexed to 90° (so the tibial tuberosity is perpendicular to the midline of the patella)
- Therapist slowly extend the patient’s knee
- As the knee is slowly extended, the Therapist observes the relative alignment of the tibial tuberosity to the midline of the patella.
- (Therapist can also palpate the movement of the tibial tuberosity).
* Since the medial femoral condyle is about 1 cm. longer than the lateral femoral condyle, the tibia first moves over the available lateral condyle surface and then must rotate laterally when we extend the knee.
* it’s impossible to perform helfet’s test if there is knee joint effusion
Positive Sign:
Absense of slight lateral tibial motion = this positive sign may indicate that a torn meniscus or injured cruciate ligament is physically blocking the knee extension.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
McMurray’s Test
Testing for:
Injury to the Menisci
Procedure:
- Patient is supine, their affected hip and knee are flexed
- Therapist cups one hand over the patient’s knee (palm over the patella and fingers/thumb over the joint line)
- Therapist grasps patient’s heel with the other hand
- Therapist slowly extends the patient’s knee, while applying different stresses (#s 1 & 2 below) to check both menisci
- external rotation of the tibia and valgus stress on the knee to assess medial meniscus
- internal rotation of the tibia and varus stress on the knee to assess lateral meniscus
Positive Sign:
Click or Catch in the extension of the knee. (A negative test does not completely rule out meniscal tear)
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Bragard’s Sign
Testing for:
Meniscal Tearing
Procedure 1: Extension of the knee and External Rotation of the Tibia
- Patient is supine with affected hip and knee flexed
- Therapist stabilizes proximal to the knee with one hand while externally rotating the tibia with the other hand = while extending the knee
Procedure 1 + Positive Sign:
– Pain or tenderness along the medial aspect of the joint line indicates medial meniscus injury.
Procedure 2: Internal Rotation of the Tibia & Extension of the knee
- Patient is supine with affected hip and knee flexed
- Therapist stabilizes proximal to the knee with one hand while internally rotating the tibia with the other hand = while extending the knee
Procedure 2 + Positive Sign :
– Pain or tenderness along the lateral aspect of the joint line indicates lateral meniscus injury.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Apley’s Compression Test (Knee)
Testing for:
Meniscal Injury
Procedure:
- Patient is prone
- Patient then flexes affected knee to 90°
- Therapist’s one hand grasps patient’s heel and ankle while the other hand stabilizes the leg
- Therapist compresses the flexed knee joint and the menisci —by pushing the patient’s foot and tibia down into the table, followed by internal and external rotation of the tibia.
Positive Sign:
Pain on the medial aspect = medial meniscus damage/injury
Pain on the lateral aspect = lateral meniscus injury/damage
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Apley’s Distraction Test
Testing for:
The Integrity of the Collateral Knee Ligaments
Procedure:
- Patient is prone, with their affected knee flexed 90°
- Therapist places their own knee on patient’s posterior thigh to stabilize
- Therapist grasps patient’s leg proximal to the ankle
- Therapist applies traction to the tibia towards the ceiling (this distracts the knee joint) —then apply internal and external rotation of the tibia while tractioning
Positive Sign:
Pain on the medial side = medial collateral ligament damage/ injury
Pain on the lateral side = lateral collateral ligament damage/ injury
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Coronary Ligamentous Stress Test
Testing for:
The integrity of the Coronary Ligament (knee)
Procedure:
- Patient is seated, their knee flexed to 90°
- Therapist passively externally rotates the tibia on the femur
Positive Sign:
Pain on external rotation of the tibia indicates coronary ligament sprain. (With sprain of the coronary ligament, valgus stress test does not cause pain).
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Clarke’s Patellofemoral Grind Test
Testing for:
Patellofemoral Syndrome
Procedure:
- Patient is supine with their knees extended
- Therapist compresses the patella posteriorly onto the femoral condyles and then, moderately move the patella distally
- Therapist instructs patient to contract the quadriceps muscles (to pull patella proximally)
Positive Sign:
Pain, crepitus, apprehension of the patient as the irritated surfaces of the patella rub over the femur.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
McConnell’s Test
Testing for:
Patellofemoral Tracking problems
Procedure:
Part I:
- Patient is seated with legs hanging over the end of the table
- Therapist sits in front of the patient
- Therapist instructs patient to externally rotate the femur of the affected leg while performing active resisted isometric contractions of the quadriceps muscles at 0, 30, 60, 90 and 120 degrees of flexion.
- Therapist notes the painful degrees/ ranges
Part II:
- Therapist passively brings the patient’s knee to full extension, resting the heel on something so the patient relaxes the quadriceps muscles
- then, Therapist glides the affected patella medially and hold the patella it in that position
- Therapist instructs patient to perform isometric contractions at the knee ranges that were painful before
Part III:
- Therapist passively brings the patient’s knee to full extension, resting the heel on something so the patient relaxes the quadriceps muscles
- then, Therapist glides the affected patella laterally and hold the patella it in that position
- Therapist instructs patient to perform isometric contractions at the knee ranges that were painful before
Positive Test:
- Pain decreases significantly after holding patella medially = patellofemoral lateral tracking problems and/or
- Pain decreases significantly after holding patella laterally = patellofemoral medial tracking problems
Ankle and Foot Special Tests:
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
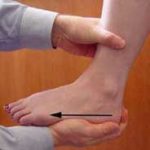
Anterior Drawer Test (Ankle)
Testing for:
Anterior Talofibular Ligament injury and/ or ligamentous instability
Procedure:
- Patient is supine with foot relaxed
- Therapist stabilizes tibia and fibula with one hand
- With the Patient’s foot plantar flexed to 20 degrees, the therapist holds the patient’s calcaneus with other hand then distracts the calcaneus from the tibia and fibula (by slowly pulling the calcanues inferiorly)
- Therapist places an anteriorly directed pressure on the calcaneus and talus, applying overpressure at the end of the passive range (stressing the Anterior Talofibular ligament)
Positive Sign:
Ligamentous laxity or rupture with Presence of sulcus and pain, and/ or Excessive anterior translation of the talus, sometimes accompanied by audible thunking
Babinski’s Test
Testing for:
Spasticity present with Central Nervous System Lesions
Procedure:
- Patient is supine
- Therapist runs a pointed object along the plantar aspect of the patient’s foot
Positive Sign:
Positive for CNS lesion = Extension of the big toe and abduction of the other toes. (Babinski Tests positive for infants up to a few weeks old and is negative after 5— 7 months.)
Deltoid Ligamentous Stress Test (Passive Relaxed)
Purpose:
To assess the deltoid ligament using 3 separate passive movements:
Procedure:
- Patient is seated with their leg flexed at the knee and hanging over a table
- Therapist stabilizes the anterior surface of the tibia and fibula proximal to the ankle (with one hand) and …
- 1. Test Anterior Fibers of the Deltoid Ligament:
- Therapist uses their other hand to graps the dorsal surface of the foot, combining eversion and plantarflexion of the foot and applying overpressure
- 2. Test Middle Fibers of the Deltoid Ligament:
- Therapist repositions their hand so the calcaneus is grasped (still stabilizing the anterior surface of the tibia and fibula proximal to the ankle with their other hand). Hindfoot is taken into eversion with overpressure
- 3. Test Posterior Fibers of the Deltoid Ligament:
- Therapist repositions their hand so the calcaneus is grasped (still stabilizing the anterior surface of the tibia and fibula proximal to the ankle with their other hand). Therapist combines eversion and dorsiflexion of the foot with overpressure
Note: to perform a general assessment of the deltoid ligament, evert the hindfoot only
Positive Sign:
Pain and Hypermobility local to the ligament
Muscle spasm end feel may be present with a subacute injury
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Functional Leg Length
Testing for:
Functional Leg length difference resulting from hip, knee or ankle and foot problems
Procedure:
- Patient stands in normal relaxed stance
- Therapist palpates ASIS and PSIS and notes any differences
- Therapist then positions the patient so that subtalar joints are neutral, toes pointed forward and the knees are straight
- Therapist re-evaluates ASIS and PSIS
Positive Sign:
Difference in leg length disappear
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Functional or Structural Pes Planus Test
Purpose:
To determine whether a pes planus is functional or structural
Procedure:
- Therapist observes (and compares) the orientation of the patient’s medial longitudinal arch while doing each of the following:
- Patient stands straight with both heels and toes on the ground
- Patient stands with just the toes on the ground
- Patient sits on the table
Positive Sign:
- Functional Pes Planus = if medial longitudinal arch is restored when the patient is either standing on the toes or seated = due to muscle or ligament weakness
- Structural Pes Planus = if medial longitudinal arch remains flat when the patient is standing on toes and when seated.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Homan’s Sign
Testing for:
The presence of Deep Vein Thrompophlebitis / Deep Vein Thrombosis
Procedure:
- patient supine with the knee extended
- patient’s foot is passively dorsi flexed
Positive Signs:
- Pain deep in the calf during dorsi flexion
also: - tenderness elicited on palpation of the calf
- pallor and swelling in leg
- loss of dorsalis pedis pulse
* massage is contraindicated with a positive test; refer patient to medical doctor
Morton’s Neuroma
Testing for:
The presence of Morton’s Neuroma
Morton’s Neuroma (is a benign neuroma of an intermetatarsal plantar nerve, most commonly of the second and third intermetatarsal spaces (between 2nd-3rd and 3rd-4th metatarsal heads). This problem is characterised by pain and/or numbness, sometimes relieved by removing footwear.
Procedure:
- Patient is seated
- Compress the foot by applying pressure to the medial and lateral aspects of the foot at the metatarsophalangel joints
Positive Sign:
Sharp pain at the location of the neuroma. Pain is worsend by activity.
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Posterior Drawer Test (Ankle)
Testing for:
Posterior Talofibular ligament injury and/or ligamentous instability
Procedure:
- Patient is supine with foot relaxed
- Therapist stabilizes tibia and fibula with one hand
- With the patient’s foot plantar flexed to 20 degrees, the Therapist holds the patient’s calcaneus with other hand then distracts the calcaneus from the tibia and fibula (by slowly pulling the calcanues inferiorly)
- Therapist places an posteriorly directed pressure on the calcaneus and talus, applying overpressure at the end of the passive range
Positive Sign:
Ligamentous laxity or rupture with Presence of sulcus and pain, and/ or
Excessive posterior translation of the talus
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Ramirez’s Test
Testing for:
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Procedure:
- Patient is supine, affected Knee in flexion (foot flat on the table)
- Wrap a blood pressure cuff around the thigh and inflate it to 40mm Hg
- Maintain the pressure for at least 2 minutes
Positive Sign:
Increase in pain as the cuff is inflated and inability to tolerate cuff inflation and sustained pressure for 2 minutes
* massage is contraindicated with a positive test; refer patient to medical doctor
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Thompson’s Test (Achilles Tendon rupture)
Testing For:
3rd degree strain or rupture of the Achilles tendon
Procedure:
- Patient is prone , feet over the edge of the table, legs relaxed
- Squeeze the affected gastrocnemius and soleus muscles
Positive Sign:
Absence of plantarflexion when the muscles are squeezed
ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS/ SPECIAL TESTS:
Tinel’s Sign (Ankle)
Testing for:
Anterior or Posterior Tibial Nerve entrapment or dysfunction
Procedure:
- Anterior tibial branch of deep peroneal nerve is tapped in front of the ankle
- The Posterior tibial nerve tapped as it passes behind the medial malleolus
Positive Sign:
Tingling or Paresthesia felt distally