 Postural Assessment
Postural Assessment
FOR Gait Assessment see: GAIT ASSESSMENT PAGE
Static Postural Assessment
Posture – a synthesis of the positions of all the body’s joints at any given time. In normal posture, gravity acts in a balanced line on the physiological curves of the spine. Shifting the body’s weight away from this line means that another region of the spine or body must compenste to regain postural stability.
***Remember to Assess All Anterior, Posterior and Bilateral Side Views, from the Feet to the Head. Postural Assessment includes assessment of all patient views.
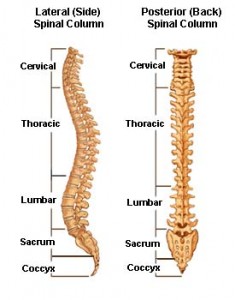
Postural Assessment: Normal Spinal Curvature:
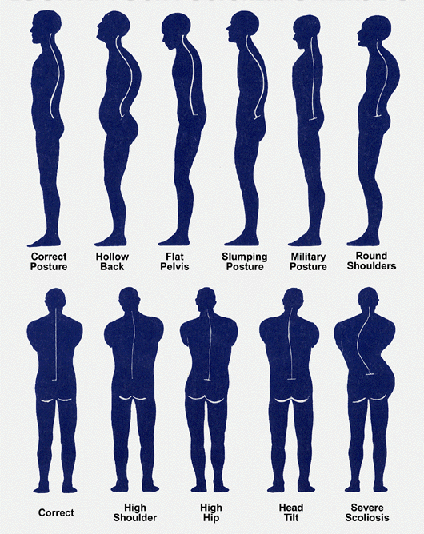
Ideal Posture
- muscles are balanced
- pelvis is neutral
- ASIS ( anterior superior iliac spine) is directly above the pubic tubercle
- earlobes are directly above the shoulders
- natural curvature of the spine and is the most efficient, least stressful posture
Postural Assessment: Abnormal Spinal Curves:
Abnormal Postures: Deviations from the Ideal Posture
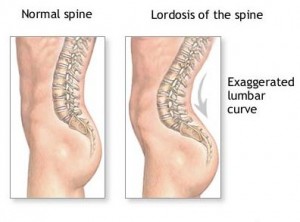
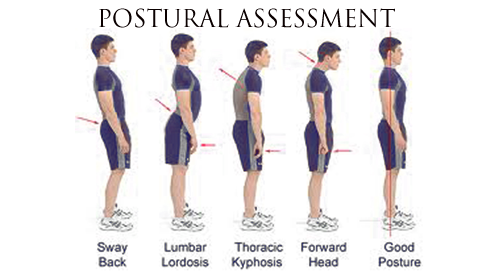
1. Lordosis is defined by an excessive inward curve of the spine. Although it primary affects the lumbar spine, it does occur in the neck too.
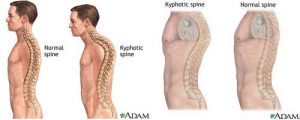
2. Kyphosis is defined by an excessive outward curve of the spine and may cause a deformity such as a humpback or hunchback. Abnormal kyphosis is more commonly found in the thoracic or thoracolumbar (chest area/low back), but can affect the neck too.
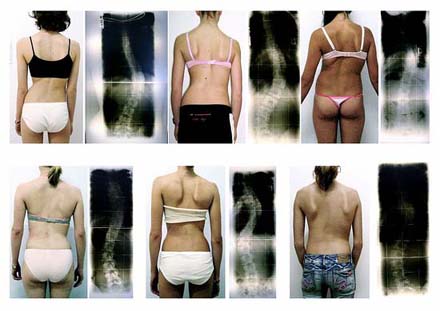
3. Scoliosis is the abnormal curving of the spine to the left or right side . Scoliosis most often affects the thoracic spine and children, although it is found in adults too.
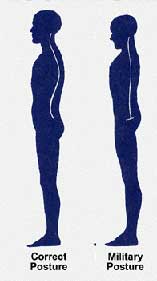
4. Military Posture – torso is pushed up and forward; anterior tilt of pelvis, knees hyperextended
- Strong/ Tight Muscles: low back and hip flexors
- Weak/ Elongated Muscles: abdominals
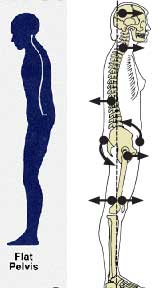
5. Flat Back Posture – head is forward; posterior tilt of pelvis; little or no curvature in the spine. A flat back posture is where the pelvis is turned under (posterior tilt) which causes the lower and upper back to have minimal curvature. This can also have a knock on effect of throwing the head forward.
- Short/Tight Muscles – abdominals, hamstrings, flexors of the neck – front & sides of the neck
- Weak/ Elongated Muscles – hip flexors, back extensors, quadriceps, lumbar erector spinae, gluteal muscles
5. Sway Back Posture – head forward; hips are thrusted forward; posterior tilt of pelvis (greater tilt than flat-back)
- Short/ Tight Muscles: hamstrings, internal obliques, low back
- Weak/ Elongated Muscles: hip flexors, external obliques, upper back extensors, neck flexors