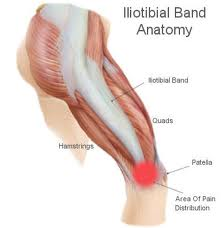
The IT Band runs down outside of the thigh from the hip to just below the side of the knee. The iliotibial band (ITB, IT Band) or iliotibial tract is a reinforced band of dense fibrous connective tissue/ fascia in the thigh connecting proximally to the Tensor Fascia Lata and Gluteus Maximus muscles, and distally to the lateral condyle of the tibia ( Gerdy’s Tubercle).
Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS or ITBFS, for iliotibial band friction syndrome) is a common injury to the knee, generally associated with running, cycling, hiking or weight-lifting (especially squats).
IT Band Massage: ITBS SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
- Pain is gradual at onset and worse with activity
- Pain felt at lateral thigh and lateral knee
- Thickening, adhesions and fibrositic nodules ( like adhesions along the fascia) of the affected IT Band ( especially in the knee area where theres a lot of movement)
- Hypertonicity and Trigger points in the Tensor Fascia Lata, gluteus maximus, hip flexors, rectus femoris leading to decrease circulation and shortening of these muscles
- Inflammation at the lateral femoral condyle due to tight IT Band. There could be rubbing and inflammation at the hip due to trochanteric bursitis
- With anterior pelvic tilt, lumbar pain and SI joint hypermobility
- Valgus or hyperextension at the affected knee
- Pes planus
Iliotibial Band Contracture & IT Band Friction Syndrome
- ITB Friction syndrome is inflammation and pain where the IT band crosses the lateral femoral condyle
- ITB contracture is the shortening or thickening of the IT band
- ITB Contracture and Friction Syndrome may occur unilaterally or bilaterally
- The fascia surrounding Glute Max and Tensor Fascia Lata (TFL) join to form the IT band
- IT band provides lateral support to the knee
- When fascia is contractured, biomechanics of the knee and hip are restricted. Ankle and SI joint may compensate
- Bursa between greater trochanter and IT band may become inflamed ( trochanteric bursitis)
- Trigger points in glute max and TFL may also contribute to ITB tightness
CAUSES of IT Band Syndrome / IT Band Contracture
IT Band Friction Syndrome
- Prolonged, repetitive activities where knee and hip are flexed — like running, cycling
- Contributing factor — poor TFL stretching procedures, anterior pelvic tilt, tight TFL, glutes
ITB Contracture
- Activities or occupations that place the knee and hip in flexion (cycling, horseback riding, prolonged sitting, running with pronated feet) and allows ITB and TFL to tightened
- Postural Imbalance — anterior pelvic tilt / hyperlordosis
- Prolonged wheelchair use, bed rest
IT Band Massage : OBSERVATION
- Hypertonic IT Band creates indentation in the lateral thigh
- Unilateral IT Band contracture, lateral pelvic tilt can be seen on the affected side
- Affected knee is valgus
- Pes planus on the affected side
- With bilateral IT Band contracture, anterior pelvic tilt due to short ITB and TFL
- Hyperlordosis from anterior pelvic tilt, short hip flexors, rectus femoris
- IT Band friction syndrome may show redness, edema at affected lateral femoral condyle
- Lateral quads and hamstrings may be tight
IT Band Massage : PALPATION
- Tenderness along IT Band, especially distal 1/3, also at greater trochanter
- Affected IT Band thickened, adhesion present
- In the affected side – hypertonicity and trigger points in the TFL and glute max.
- On non — affected side – hypertonicity and trigger points in the hip flexors
- If bilateral, hypertonicity and trigger points in TFL, glute max, rectus femoris, iliopsoas, adductors and Quadratus Lumborum
- With friction syndrome, inflammation, heat, swelling, point tenderness local to the lateral femoral condyle area
IT Band Massage : ROM TESTING
- Active Free ROM of affected knee, hip, SI joint and Lumbar Spine
- Reduced extension and adduction of hip
- Painful knee extension with friction syndrome ( esp. in the act of extending the knee — tight band snaps to the lateral femoral condyle)
- Passive Relaxed ROM of affected knee, hip, SI joint
- Painful at lateral knee with extension
- Active Resisted testing of TFL, rectus femoris, glute max, glute medius, iliopsoas, Quadratus Lumborum
IT Band Massage : SPECIAL Orthopedic TESTING
- Thomas Test — tight ITB, TFL, rectus femoris
- Ely’s Test — right rectus femoris
- Ober’s and Modified Obers — tight ITB, TFL
- Noble’s Test
IT Band Massage Therapy Treatment
- Fascial Techniques to ITB, in various directions and interspersed with effleurage ( to drain and because fascial work there is painful)
- Skin rolling, Cross-hand spreading, C and S bowing techniques, J stroke
- Cross fiber friction to adhesions, followed by ice and stretch
- If friction syndrome is present, inflammation at lateral femoral condyle makes onsite fascial technique impossible. Use ice local. Working on proximal IT Band can reduce tightness in the distal IT Band until inflammation is gone and on-site work is possible.
- TFL muscle massage: treat hypertonicity, adhesion, trigger points by ( skin rolling, petrissage, stripping to attachment at iliac crest and around trochanter, GTO at trochanter where TFL distal musculotendinous junction located)
- Glute max: massage for hypertonicity and trigger points
- Repetitive effleurage to lateral leg and glutes to increase circulation
- Contrast hydro can improve circulation
- Rest of affected leg: treat iliopsoas, quads, hamstrings, adductors, muscles of lower leg
- Passive Relaxed ROM of hip and knee. Ankle, knee, hip, SI joint treatment with joint play itb massage, masage for itband, itband massage therapy, massage therapy for it band, massage treatment itb, massage treatment itband
IT Band Massage: SELF CARE
- Deep moist heat to loosen IT Band ( if there is no inflammation)
- Contrast hydrotherapy to increase circulation
- Ice to lateral femoral condyle with acute friction syndrome
- Self massage to IT Band and TFL (foam roller)
- Stretch TFL, especially if seated for long periods. ( with arms raised, affected leg behind, front leg lunged down, bend sideways)