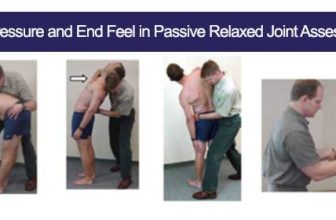
Normal End Feel
Normal End Feel is when the joint has full range of motion and the range is stopped by the anatomy of the joint.
Bony End Feel (Bone to Bone)
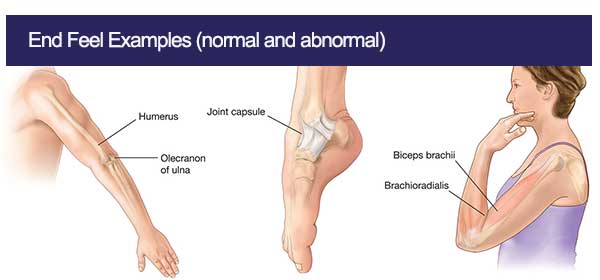
End feel occurs when bone contracts bone at the end of normal range, as in the extension of the elbow. Normal bony end feel is abrupt and hard but not painful.
Sensation of Normal Bony End Feel
Therapist’s Perspective
Sensation: A hard, unyielding, and abrupt stop with no give.
Example: Elbow Extension – The olecranon process contacts the olecranon fossa, creating a firm, clear stop.
Patient’s Perspective
Feels like a painless, firm stop at the end of the motion, feeling like the joint has reached its natural limit.
Example: Elbow Extension – The elbow stops extending without pain or discomfort.
3 Examples of Normal Bony End Feel
- Elbow Extension – When fully extending the elbow, you feel the olecranon process of the ulna hit the olecranon fossa of the humerus, resulting in a clear, firm, and painless stop.
- Radial Deviation of the Wrist – As the wrist is radially deviated, the radial styloid process contacts the scaphoid, creating a hard end feel.
- Knee Extension – Full extension of the knee leads to contact between the femoral and tibial condyles, resulting in a hard, abrupt sensation.
Soft Tissue Approximation
End feel occurs when the full range of the joint is restricted by the normal muscle bulk. For the therapist, normal soft tissue approximation has a feeling of soft compression. For the client, it is painless.
Sensation of Normal Soft Tissue Approximation
Therapist’s Perspective
A soft, yielding compression as soft tissues (muscles) press against each other. For example, in elbow flexion, the biceps bulk compresses against the forearm muscles, resulting in a cushioned stop.
Patient’s Perspective
A compression that is cushioned and painless. It feels like two soft surfaces pressing against each other. A soft, comfortable feeling of muscles pressing together, limiting further movement. In elbow flexion, the forearm contacts the biceps, stopping movement gently without pain.
3 Examples Normal Soft Tissue Approximation
- Elbow Flexion (Biceps) – Flexing the elbow causes the biceps muscle to contact the forearm muscles, producing a soft compression that is painless. When flexing the elbow, the bulk of the biceps muscle presses against the forearm muscles, creating a gentle, yielding stop due to the tissue compression.
- Knee Flexion – When the knee is fully flexed, the calf muscles contact the back of the thigh, leading to a soft, cushioned end feel.
- Hip Flexion with Knee Flexion – Flexing the hip with the knee also flexed results in the thigh contacting the abdomen, creating a soft tissue approximation.
Tissue Stretch (aka Muscular Stretch)
End feel occurs at the extremes of muscle stretch, such as the hamstring stretch when performing the straight leg raise test.
For the therapist, normal tissue stretch has a feeling of increasing tension, springiness or elasticity. The patient may feel a stretching sensation.
Sensation of Normal Tissue Stretch
Therapist’s Perspective
A firm, springy resistance with a slight give towards the end of the range of motion. It feels elastic, as though the tissues are being stretched but not overextended. For example, in lateral flexion of the Cervical Spine, the tissues provide elastic resistance as they stretch.
Patient’s Perspective
Firm but comfortable stretch, similar to a gentle pulling, without pain. For example in the lateral flexion of the neck, the neck stretches to its limit with a springy feel.
3 Examples Normal Tissue Stretch
- Lateral Flexion of the Cervical Spine – When laterally flexing the cervical spine, you feel a firm, springy resistance as the muscles and ligaments stretch, providing a controlled stop.
- Wrist Flexion – Flexing the wrist results in a firm, springy end feel due to the stretching of the flexor tendons and ligaments.
- Ankle Dorsiflexion – Dorsiflexing the ankle produces a firm, elastic resistance as the Achilles tendon and calf muscles are stretched.
Capsular Stretch/ Leathery End Feel
End feel occurs when the joint capsule is stretched at the end of its normal range, such as with external rotation of the shoulder joint.
for the therapist, normal capsular stretch feels like stretching a pience of leather. For the patient, it is painless.
A capsular pattern is the pattern of limitation of movement at an injured joint. With injury to the joint capsule or the synovial lining, a pattern of proportional limitation will be noted as the therapist takes the joint through its passive range. The limitation is due either to fibrosing/ thickening of the joint capsule , to inflammation or to joint swelling (joint effusion).
A non- capsular pattern is limitation of movement of a joint but not in a capsular pattern. This restriction may be due to an intra-articular mechanical blockage from torn pieces of cartilage, minisci or intra articular adhesions. it may be due to extra capsular lesions such as muscle contracture, myositis ossificans or acute bursitis
Sensation of Normal Capsular Stretch/ Leathery End Feel
Therapist’s Perspective
A firm, leathery resistance that occurs at the end of the normal range of motion. It feels like stretching a piece of leather, with a slight but distinct give. This end feel is smooth and consistent, indicating the normal tension of the joint capsule.
Patient’s Perspective
A firm and comfortable stretch at the end of the joint’s range, similar to stretching a band but without pain. The feeling is of a natural limit being reached, with no discomfort or sharp sensations.
3 Examples Normal Capsular Stretch/ Leathery End Feel
- Glenohumeral Joint External Rotation: The shoulder’s external rotation feels firm and smooth as the capsule stretches. The patient feels a firm, comfortable stretch when the shoulder is externally rotated fully.
- Hip Extension: The hip joint’s anterior capsule feels firm and leathery as it reaches full extension. When extending the hip, the therapist feels a firm, leathery resistance as the anterior capsule stretches.
- Wrist Extension: When extending the wrist, a firm, leathery resistance is felt as the joint capsule stretches at the end of its range.
Abnormal End Feels
Boggy or Soft End Feel
Boggy or Soft End Feel occurs with edema or joint effusion (When too much fluid builds up around a joint ). It has a mushy or soft quality to it with no clear resistance. In the case of ligament injury, such as in a moderate to severe pain, a softer end feel is encountered by the therapist, until the slack is taken up by other structures.
Cause: Joint effusion, edema, or acute inflammation.
Sensation of Abnormal Boggy or Soft End Feel
Therapist’s Perspective
A soft, mushy stop with no clear resistance, indicating fluid or swelling. For example, in knee flexion with joint effusion there is a soft, yielding sensation during flexion.
Patient’s Perspective
It feels like pressing into a water balloon, indicating fluid accumulation within the joint. A squishy, swollen feeling, often accompanied by discomfort or pain. For example, in knee flexion with joint effusion, it feels like moving through fluid, with discomfort.
3 Examples of Abnormal Boggy or Soft End Feel
- Knee Flexion with Joint Effusion – The movement feels soft and mushy due to the presence of excess fluid within the knee joint.
- Ankle Plantarflexion with Acute Ligamentous Injury – A soft, boggy sensation is felt due to swelling from a recent ligament sprain.
- Elbow Extension with Severe Edema – Significant swelling in the elbow joint results in a soft, boggy end feel during extension.
Bony End Feel (Bone to Bone)
Bony End Feel occuring before a normal range, indicates bony changes such as presence of osteophytes with degenerative joint disease or malunion of a joint following a fracture.
Cause: Osteophytes, degenerative joint disease, or mal-union after a fracture.
Sensation of Abnormal Bony End Feel
Therapist’s Perspective
A hard, unyielding stop occurring earlier than expected. For example, in elbow flexion with osteophytes, a hard stop occurs before normal flexion range.
Patient’s Perspective
A premature hard stop, possibly accompanied by discomfort.
3 Examples of Abnormal Bony End Feel
- Elbow Flexion with Osteophytes – The presence of osteophytes in the elbow joint creates an unexpected hard, unyielding end feel before reaching the normal range of motion.
- Knee Extension with Osteoarthritis – Degenerative joint disease in the knee can lead to an early, hard end feel due to bony changes.
- Wrist Extension after Fracture Mal-Union – Improper healing of a fractured wrist can cause a bony end feel where it would not normally occur.
Capsular Stretch End Feel (Leathery End Feel)
Capsular Stretch or Leathery End Feel – occurs before normal range. It might indicate capsular fibrosis if a capsular pattern of restriction is present with no inflammation.
Cause: Joint capsule stiffness or chronic inflammation.
Sensation of Abnormal Leathery End Feel (Capsular Stretch End Feel)
Therapist’s Perspective
A firm, leathery resistance with reduced range of motion. An example is shoulder external rotation with Adhesive Capsulitis – early, firm stop due to capsular tightness. Similar to tissue stretch but with reduced range of motion. It feels firm and leathery, with the resistance coming on more abruptly (hard capsular) or gradually (soft capsular).
Patient’s Perspective
A firm, stiff feeling limiting movement, often with some discomfort. An example is shoulder external rotation with Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen shoulder) – stiff and resistant to movement.
3 Examples of Abnormal Leathery End Feel (Capsular Stretch End Feel)
- Shoulder External Rotation with Adhesive Capsulitis – The movement is restricted with a firm, leathery feel due to the thickened shoulder joint capsule.
- Hip Extension with Capsular Tightness – A hard, capsular end feel occurs prematurely due to hip joint capsule stiffness.
- Ankle Plantarflexion with Chronic Capsulitis – The end feel is leathery and occurs earlier than expected due to chronic inflammation and fibrosis of the ankle joint capsule.
Empty End Feel
Empty End feel occurs when there is no physical restriction to movement except the pain perceived by the patient. This indicates joint inflammation or bursitis.
Cause: Conditions like acute bursitis or severe joint inflammation.
Sensation of Empty End Feel
Therapist’s Perspective
No physical restriction, but movement is halted due to patient pain. An example is shoulder abduction with Acute Bursitis. There would be no resistance felt, but patient experiences pain before the end of range.
Patient’s Perspective
No physical restriction to movement, but considerable pain prevents further motion. It feels like you could continue moving the joint if not for the pain.
3 Examples of Empty End Feel
- Shoulder Abduction with Acute Bursitis – The patient experiences significant pain before reaching the end of the range, with no resistance felt by the therapist. The range of motion seems unrestricted mechanically, but the patient’s pain stops the movement.
- Hip Flexion with Severe Inflammation – Pain prevents the patient from allowing full range of motion despite the absence of physical restriction.
- Knee Extension with Acute Synovitis – Considerable pain stops the movement early, even though the joint itself has no mechanical block.
Muscle Spasm End Feel
Muscle Spasm end feel occurs when passive movement stops abruptly with some springy rebound and pain. This is a result of reflexive muscle spasm, which is designed to prevent further injury. It also indicates synovial inflammation when felt with a capsular pattern of restriction.
Cause: Protective muscle guarding in response to pain or injury.
Sensation of Abnormal Muscle Spasm End Feel
Therapist’s Perspective
A sudden, hard stop with muscle contraction and pain. An example would be cervical rotation with acute neck pain – movement stops suddenly due to muscle spasm.
Patient’s Perspective
Sudden pain and a feeling of muscles locking up, preventing further movement. For example, sharp pain and a sudden stop when trying to rotate the neck to look right or left.
3 Examples of Abnormal Muscle Spasm End Feel
- Acute Low Back Pain – Attempting to flex the lumbar spine can cause a sudden, hard arrest of movement with pain. If a disc slips from its place between vertebrae and pinches a nerve, the electrical signals that move from the nerve to nearby muscle tissue may be disrupted, leading to painful muscle spasms.
- Cervical Muscle Spasm – Rotation of the cervical spine may be abruptly halted by a painful, protective muscle spasm from a whiplash injury.
- Shoulder Abduction – Acute shoulder injury can lead to a sudden, painful stop in movement due to muscle guarding.
Sensation: A sudden, hard, dramatic arrest of movement, often accompanied by pain. It feels like a reflexive, protective muscle contraction that stops the motion abruptly.
Springy Block End Feel/ Internal Derangement End Feel
Springy block or internal derangement end feel is a springy or rebounding sensation in a non-capsular pattern . This indicates loose cartilage or meniscal tissue within the joint.
Cause: Loose bodies, torn meniscus, or other intra-articular derangements.
Sensation of Abnormal Springy Block End Feel/ Internal Derangement End Feel
Therapist’s Perspective
A bouncy, springy stop before normal range, indicating internal obstruction such as a loose body or a displaced piece of cartilage. For example, with a torn meniscus, extending the knee will cause springy resistance during extension. When you move the joint passively, you feel a distinct, bouncy resistance that prevents further motion. This springy stop occurs before reaching the normal range of motion, indicating that something within the joint is obstructing movement. The resistance feels like a soft rebound or a mechanical block that has some give, unlike the hard stop of a bony end feel.
Patient’s Perspective
As the joint is moved, a patient might experience a sudden, bouncy stop that feels like something is blocking the motion. This sensation is usually accompanied by discomfort or a sense of something moving or shifting inside the joint. It feels like the joint is being gently but firmly rebounded back. For example, with knee extension with a torn meniscus, when trying to extend the knee, a patient might feel a bouncy resistance and a sense of something catching or obstructing the movement, often leading to discomfort.
3 Examples of Abnormal Springy Block End Feel/ Internal Derangement End Feel
- Knee Extension with Torn Meniscus – A springy, rebound sensation occurs when trying to fully extend the knee, caused by the displaced meniscal tissue.
- Elbow Flexion with Loose Cartilage – Loose bodies in the elbow joint cause a springy block before reaching the normal end range.
- Ankle Dorsiflexion with Joint Fragment – A springy sensation is felt when the joint fragment obstructs normal motion.