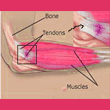
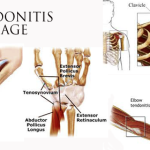
 Tendinitis / Tendonitis is an inflammation of a tendon. By nature, tendinitis is a chronic condition with an initial acute inflammatory stage.
Tendinitis / Tendonitis is an inflammation of a tendon. By nature, tendinitis is a chronic condition with an initial acute inflammatory stage.
Tendons are made up of dense collagen fibers, and attach muscles to bones. They have limited blood supply, and their health can be easily compromised in the areas of friction and compression. When a tendon gets injured, the limited blood supply causes the slow healing process of the tendons.
TENDONITIS MASSAGE THERAPY TREATMENT:
Acute Tendonitis Massage: Tendinitis massage wrist tendonitis massage elbow tendinitis
- Limb elevated (if really inflamed), cold hydro applied to affected tendon
- MLD ( manual lymphatic drainage to proximal limb)
- Treat proximal limb for hypertonicity
- Ischemic compressions to trigger point referring to the lesion site
- Treat hypertonicity in antagonists of affected muscles, DO NOT flush toward the lesion site(use segmental instead of long strokes)
- Treat hypertonicity of Affected muscles using GTO on unaffected tendon
- Muscle squeezing and stroking to distal limb
- Pain free Passive Relaxed ROM on proximal and affected joint to maintain succusive action
- Gentle joint play to affected limb
Chronic Tendonitis Massage Therapy Treatment: Tendinitis massage wrist tendonitis massage
- Position for comfort
- Hydro is local deep moist heat ( to soften adhesion and increase circulation)
- If chronic edema remains, begin with fascial work to loosen area, follow with contrast hydro to flush it out
- Proximal limb treated to increase circulation and to decrease: hypertonicity and trigger points
- Antagonists treated with skin rolling, long effleurage, pettrisage to increase circulation
- Affected muscle treated, working toward the lesion
- Adhesions may form between tendons and paratendons or at musculocutaneous junctions. Tendon is located by asking client to contract affected muscle.
- Skin rolling, fascial spreading and muscle stripping used to decrease adhesions before cross fiber friction technique is used
- Frictions applied across tender adhesions. If tendon adhered to sheath, a stretch must be placed on the tendon while frictions is performed to allow the sheath to be mobilized away from the tendon ( ex. Biceps tendon)
- Follow frictions with passive stretch and ice
- Distal limb may be treated with effleurage and petrissage
- Joint play and Passive ROM to affected limb
- Passive stretch to affected muscles
Considerations and Contraindications for Tendonitis Massage Therapy Treatment:
- NO Frictions when client is taking anti-inflammatories
- If client is taking anti-inflammatories, therapist uses only fascial techniques & muscle stripping to decrease adhesions in the tendons
- Avoid techniques that increase circulation to the lesion site
- Do not flush toward the lesion site
Tendonitis contraindication tendinitis contraindicated massage contraindicated tendonitis
Signs And Symptoms of Tendonitis:
Grades of Tendinitis: Tendinitis massage wrist tendonitis massage elbow tendinitis
Grade 1 Tendonitis: pain after activity only
Grade 2 Tendonitis: pain at the beginning of activity, disappears with activity, returns afterwards
Grade 3 Tendonitis: pain at the beginning, during, and after activity; pain may restrict activity
Grade 4 Tendonitis: pain with activities of daily living, and to get worse
Acute Tendonitis: Tendinitis massage wrist tendonitis massage elbow tendinitis
- Gradual onset, tenderness local to the tendon one or two days after activity. The tenderness progresses into pain during activity as the tendonitis becomes severe.
- Microtearing causes a cycle of inflammation and the formation of adhesions and even crepitus in the area
- Inflammation, heat and swelling at the tendon or sheath
- Decreased ROM of affected muscles
Chronic Tendonitis: Tendinitis massage wrist tendonitis massage elbow tendinitis
- Pain during and after activity
- Chronic inflammation, adhesions, crepitus and fibrosis present
- Chronic swelling, thickening may be visible if the tendon is superficial
- Decrease in ROM and strength of the affected muscles
- Flare —ups to acute stage may occur with repeated overuse
- Tendons may degenerate until rupture occurs
Self Care for Tendonitis:
Acute Tendonitis: Tendinitis massage wrist tendonitis massage elbow tendinitis
- Relative rest from the cause of tendinitis. Rest continues until pain and inflammation decreases. This prevents the tendonitis from becoming chronic.
- Hydro is ice immediately after activity. 5-20 mins.
- Slow pain-free stretch to affected muscles to increase flexibility
- When pain is gone before, during and after activity, Begin with pain-free isometric exercise, then strengthening of the muscles to regain full strength of the muscle and to prevent reinjury
Chronic Tendonitis: Tendinitis massage wrist tendonitis massage elbow tendinitis
- Contrast Hydro to increase tissue health. Ice during flare up
- Self massage to affected muscles and antagonists
- Stretching continued from acute stage, & strengthening can be isotonic.
- Eccentric exercise appears to have specific strengthening effect on tendons
- Client should work up to 3 sets of 15 reps of isotonic exercises for affected muscles
- Modify sport or occupational activity to reduce repetition & speed
- Exercise routine, including stretching